
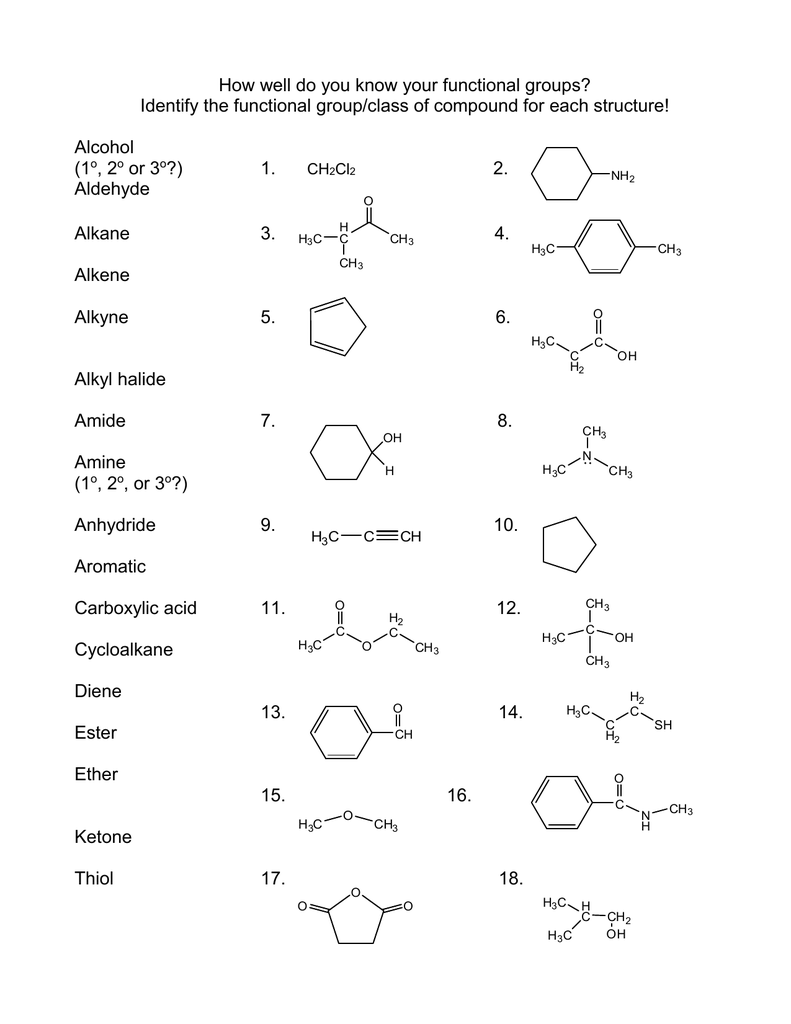
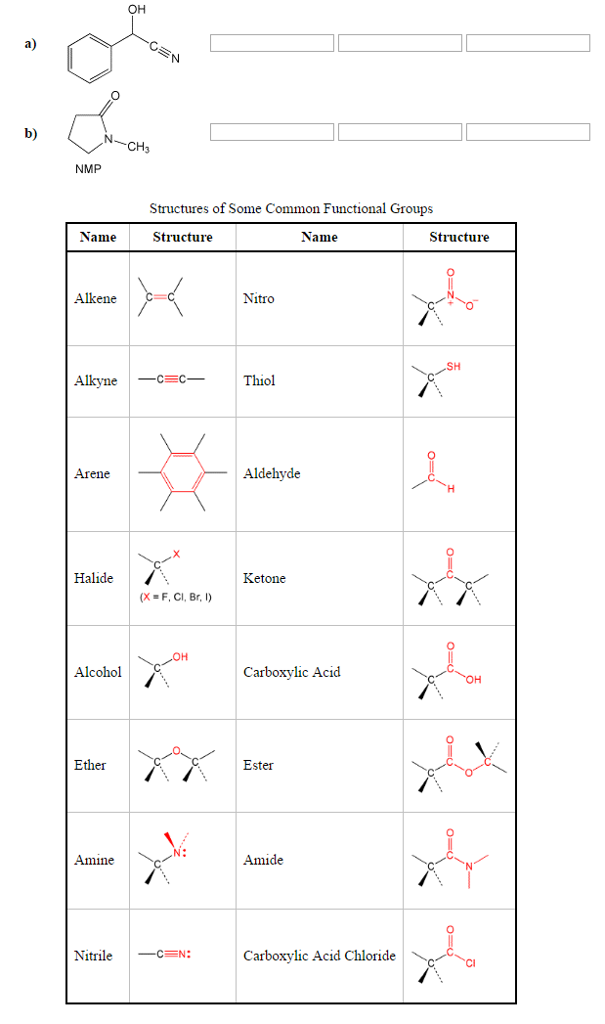
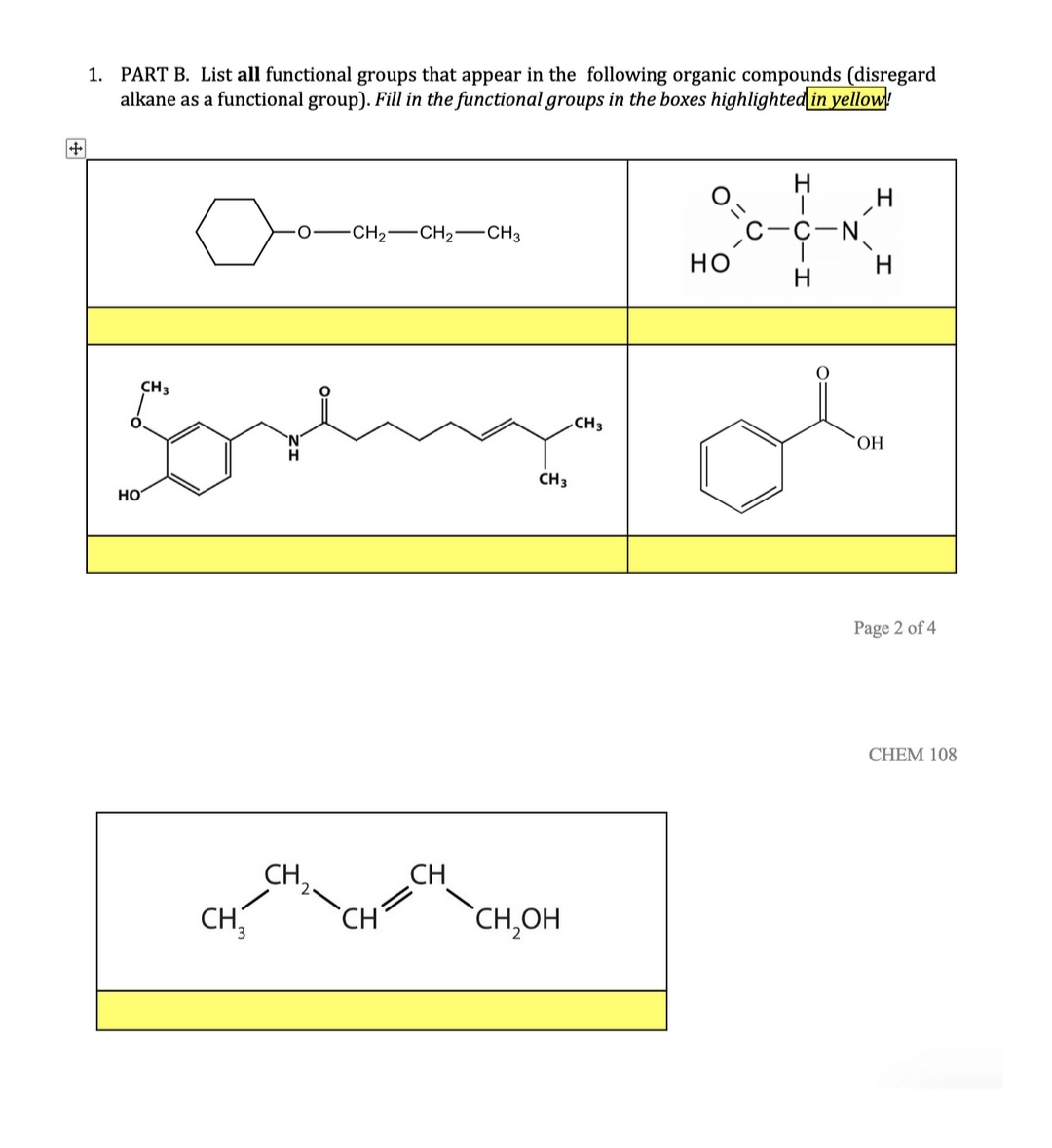
The –R–O–R– group is the functional group of an ether.Īldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Estersįunctional groups related to the carbonyl group include the –CHO group of an aldehyde, the –CO– group of a ketone, the –COOH group of a carboxylic acid, and the –COOR group of an ester. The –OH group, known as a hydroxyl group, is the functional group of an alcohol. The properties of hydrocarbon derivatives are determined largely by the functional group. A hydrocarbon derivative can be formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon with a functional group, which contains at least one atom of an element other than carbon or hydrogen. Many organic compounds that are not hydrocarbons can be thought of as derivatives of hydrocarbons. Aromatic hydrocarbons contain ring structures. Alkynes contain one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds. Alkenes contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. The alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons-that is, hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen. The chemistry of these compounds is called organic chemistry. Strong, stable bonds between carbon atoms produce complex molecules containing chains, branches, and rings. Each functional group is a unique arrangement of atoms and is assigned a name for the combination of atoms that make up the group. These functional groups are an indispensable part of organic chemistry and important components of biological molecules, such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. For example, the presence of certain functional groups on a molecule will make them hydrophilic, whereas others will make them hydrophobic. It can also be attached to proteins to alter their function.įunctional groups are a group of atoms with characteristic properties, which when linked to the carbon skeleton of a molecule, alter the properties of that molecule. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.Ī phosphate group is a phosphorus bonded to four oxygens and is commonly found in DNA, the genetic material of all living organisms. An amine has a nitrogen with a lone pair linked to a combination of hydrogens and R groups. Lipids contain esters, and amino acids contain carboxylic acids.Īmino acids also have another common functional group called an amine or amino group. R groups often represent hydrocarbons but can be other groups or atoms.Īldehydes and ketones are key functional groups in carbohydratesĮsters consist of a carbonyl group flanked by a R group and an oxygen, while carboxylic acids, or carboxyl groups, are flanked by an R group and an alcohol. Carbonyl containing groups include functional groups such as aldehydes, ketones, esters, and carboxyl groups.Īldehydes have hydrogen and a variable or R group attached to a carbonyl, while ketones have two variable groups. It is an important constituent of several compounds, such as methanol, water, and carbohydrates.Īnother category of functional groups is the carbonyl groups, which contain a carbon and an oxygen linked together by a double bond. One of the simplest non-carbon containing groups is the hydroxyl group which contains an oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom. If the carbons are linked together by alternating single and double bonds, it is called an aromatic ring or an aryl group. If the ring contains only single bonds, it is called a cycloalkane. Carbon atoms in alkanes are linked together by single bonds, whereas alkenes and alkynes contain double or triple bonds, respectively. These include alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. Hydrocarbons are the basis of organic molecules and contain varying numbers of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Naming functional groups allows for the quick identification of the atoms in a molecule, which is useful in organic chemistry and biochemistry. Molecules containing the same functional groups often exhibit similar properties and undergo similar reactions. Functional groups are covalently bonded sets of atoms that affect the properties of a molecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
